Typhoon - Dependency Injection with Swift
April 14, 2015
Dependency Injection
marvel
swift
typhoon
Dependency Injection is a useful design pattern that allows for an application to be decoupled and it simplifies testing. It is used in the Java world with frameworks like Spring and Guice. In Swift one Dependency Injection container is Typhoon. This article will show how to incorporate Typhoon in an application.
Let’s start with the code from this article. It is a very simple application that accesses the developer API of Marvel to download images of a character.
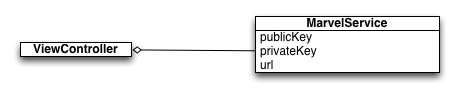
The ViewController class uses a MarvelService which has three properties; public key, private key and url. The MarvelService is the class that is responsible for interfacing with the Marvel API. Our first step will be injecting the MarvelService into the ViewController.
To get the sample code running, you will need a few things installed first.
Prerequisites
- XCode 6.3
- Cocoapods
- Git
1.Checkout the code from github and use the typhoon branch. The dependencies have be defined in Podfile.
2.Open the project and look inside the ViewController class and the download method.
It will look like the following:
var marvelService = MarvelService()
marvelService.download(name!, completeCallback: {(image: UIImage) in
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue()) {
self.imageView.image = image
}
})
3.We will now get Typhoon to dependency inject the MarvelService dependency.
Open up the ViewController class and create a couple of properties that will be injected.
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var imageView: UIImageView!
var marvelService: MarvelService?
var name: String?
...
This is the updated download method.
@IBAction func download(sender: AnyObject) {
marvelService!.download(name!, completeCallback: {(image: UIImage) in
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue()) {
self.imageView.image = image
}
})
}
4.Let’s change the MarvelService so that its properties can be dependency injected.
class MarvelService :NSObject {
var publicKey: String?
var privateKey: String?
var url: String?
...
Also you will need to change the download function to deal with the optionals of the properties.
func download(name: String, completeCallback: UIImage -> () ) {
var request = HTTPTask()
request.responseSerializer = JSONResponseSerializer()
let ts = NSDate().timeIntervalSince1970.description
let hash = "\(ts)\(privateKey!)\(publicKey!)".md5()
request.GET(url!, parameters: ["nameStartsWith": name, "apikey": publicKey!, "ts" : ts, "hash": hash], success: { (response: HTTPResponse) -> Void in
if (response.responseObject != nil) {
let character = Character(JSONDecoder(response.responseObject!))
self.downloadCharacterImage(character, completeCallback: completeCallback)
}
},failure: {(error: NSError, response: HTTPResponse?) -> Void in
println("got an error: \(error)")
})
}
5.Create a configuration.plist file that will contain the String properties of the application.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>url</key>
<string>http://gateway.marvel.com:80/v1/public/characters</string>
<key>api.public.key</key>
<string>FILL IN YOUR OWN</string>
<key>api.private.key</key>
<string>FILL IN YOUR OWN</string>
<key>name</key>
<string>Ant-Man</string>
</dict>
</plist>
Make sure you fill in your own public and private keys that you get from the http://developer.marvel.com site.
6.The last piece is defining the Typhoon assembly. This is where the configuration of the dependencies will take place.
We will define 3 dependencies in the assembly the marvel Service, config and viewController. Open up the MarvelAssembly class.
The configuration is defined as the follows. This will make the properties available to be injected in the Configuration.plist.
public dynamic func config() -> AnyObject {
return TyphoonDefinition.configDefinitionWithName("Configuration.plist")
}
Let’s define the MarvelService and its dependencies.
public dynamic func marvelService() -> AnyObject {
return TyphoonDefinition.withClass(MarvelService.self) {
(definition) in
definition.injectProperty("url", with:TyphoonConfig("url"))
definition.injectProperty("publicKey", with:TyphoonConfig("api.public.key"))
definition.injectProperty("privateKey", with:TyphoonConfig("api.private.key"))
}
}
The last class is the ViewController.
public dynamic func viewController() -> AnyObject {
return TyphoonDefinition.withClass(ViewController.self) {
(definition) in
definition.injectProperty("marvelService", with:self.marvelService())
definition.injectProperty("name", with:TyphoonConfig("name"))
definition.scope = TyphoonScope.Singleton
}
}
This article has shown you how to take an dependency and inject its dependencies. This is a much more flexible and testable way of dealing with dependencies.
Here are some references.